Step-by-Step Guide to Building a Private Blockchain for Maximum Security
May 16,2025
Step-by-Step Guide to Building a Private Blockchain for Maximum Security
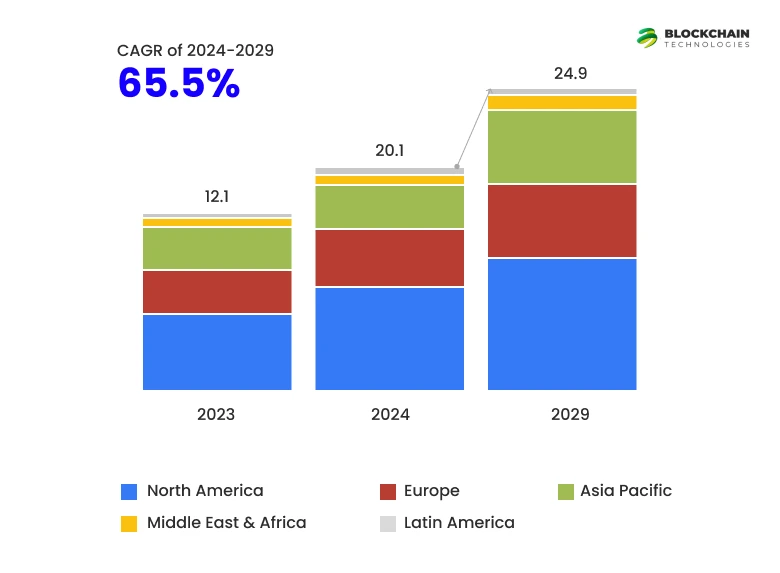
In an era of rising data breaches and cyber threats, businesses are starting to use private blockchain development services to safeguard their businesses. From new tech startups to evolving enterprises, private blockchain development services are quickly gaining traction as a stable, secure structured solution to the world’s modern data problems. With custom blockchain networks addressing the elements of control, compliance, and speed to provide a trusted infrastructure from the ground up. MarketsandMarkets states that the global blockchain market size is expected to increase from $7.4 billion in 2022 to $94.0 billion by 2027 at a CAGR of 66.2%. This says a lot about the importance of blockchain in modern business infrastructures.
This blog will take you through the complete, step-by-step process of creating a private blockchain from scratch, specifically designed for those businesses that want the security, control and scalability provided by blockchain. Whether you are a startup looking for enterprise blockchain solutions or an established company exploring a custom blockchain network setup, this series will provide all the relevant information you will need.
Before we get too far into the technical process and implementation steps, let’s first understand a little about what a private blockchain is and why it is quickly becoming the solution for enterprises around the world.
What is Private Blockchain?
A private blockchain is a permissioned blockchain network, with restricted access only to approved users. Private blockchains enhance privacy, transaction speed, and control relative to public blockchains, which can be useful to organizations looking for private blockchain solutions.
Ready to build your secure private blockchain network?
Partner with our private blockchain development company to design a secure, custom blockchain solution for your startup or enterprise.
Key Features of Private Blockchain Development
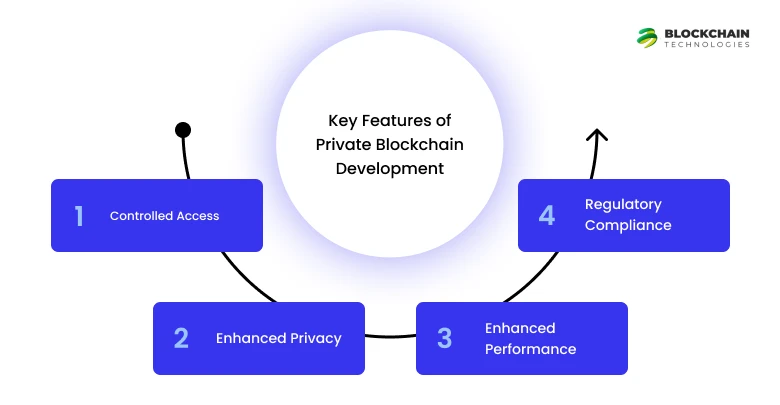
1. Controlled Access
Private blockchains are established with permissioned structures that create a framework for verified and authenticated parties that can join the network. Only verified participants can access or contribute to or validate transactions in the network, creating controls around access and credibility. For enterprises that have inherent governance and control around their data and transaction flows, this level of access control is suited to those tasks.
2. Enhanced Privacy
While public blockchains allow for all data to be receivable by anyone, private blockchains are designed to cater for confidentiality and functionality of data. Limitations on viewability of data can account to roles and departments in the private blockchain reporting. Restrictive access ensures that real businesses and real collaboration can happen and sensitive business intelligence is retained by those with permissions. Encryption and access controls deepen the tool to enhance privacy.
3. Enhanced Performance
As private blockchains include a designated set of known validators, they can leverage more efficient consensus methods like Proof of Authority (PoA) and Practical Byzantine Fault Tolerance (PBFT), resulting in better performance through minimized latency and high throughput. This makes private blockchains excellent for enterprise applications that require real time data such as supply chain management, banking transactions, or digital identity authentication.
4. Regulatory Compliance
Private blockchain frameworks allow organizations to configure the environment for their network, reflecting regulatory or corporate mandates. Whether it be KYC/AML, audit while transacting or building or some other governance model, companies can build a compliant ecosystem on the private blockchain with control over access, transactional validation, and data view.
Reasons for Opting a Private Blockchain Development for Your Business

Companies decide to use private blockchains when they want to:
1. Preserve Data Privacy and Control
Private blockchains are suited for organizations that deal with sensitive or proprietary information, such as financial records, patient health information, or intellectual property. Access to the information on a private network is limited to a select group of authorized participants instead of being accessible to the entire public like a public blockchain. A private blockchain preserves end-to-end confidentiality, incorporates data sovereignty, and potentially limits the unauthorized exposure of your sensitive information.
2. Increase Operating Efficiency
By eliminating the unnecessary middleman and by using smart contracts to automate processes, private blockchains can greatly reduce the overwrite of business processes and workflows. With fewer nodes and fast consensus mechanisms, transactions can finish much more quickly, including real-time tracking of transactions, and an automated audit trail which can reduce costs and time turnaround when executing business transactions.
3. Ensure Regulatory Compliance
For industries such as Finance, Healthcare, and Supply Chain, regulatory compliance is a must. Private blockchain networks offer built-in features for implementing role-based permissions, tracking usage history, and facilitating KYC/AML processes, all of which can help practitioners with regulatory compliance and responding to audits/policy changes at the structural-level — rather than the individual compliance-level required by practice.
4. Enable Tailor-Made Business Solutions
Private Blockchain Development: Step-by-Step Setup Guide

Building a private blockchain takes a number of steps including planning and design, development, and deployment. In this detailed guide, you’ll understand how to build a private blockchain.
1. Define requirements and use case(s)
- Identify the use case: For an effective custom blockchain network setup for enterprises, it's crucial to clearly define your objectives and expected outcomes upfront.
- Identify the participants:Who will be able to participate in the network? (i.e. organizations, users, etc.)
- Define the rules: What are the rules for accessing the blockchain, validating transactions, and permissions for each node.
2. Identify a consensus mechanism
Consensus algorithms could be based on to determine the best approach for a private blockchain:
Select an Algorithm: Choose a consensus mechanism suitable for a private blockchain, such as:
- Proof of Authority (PoA): It requires pre-authorized (or approved) nodes to validate a transaction.
- Proof of Stake (PoS): a rewarded staking-based consensus protocol for trusted participants.
- Byzantine Fault Tolerance (BFT): A system design to ensure consensus with possible faults by some nodes.
Individualize the consensus mechanism to your needs.
3. Identify a blockchain platform
Identify an existing framework to help reduce the workload:
- Hyperledger Fabric: A leading private blockchain framework.
- Ethereum Private Network: A private network protocol from Ethereum.
- Corda: An enterprise quality private blockchain protocol.
- Quorum: A private blockchain for enterprise that focuses on privacy.
| Platform | Best For | Consensus Mechanism | Strengths | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hyperledger Fabric | Large enterprises with complex needs | PBFT, Solo, Raft, Kafka | Modular architecture, fine-grained access control, strong community support | Steep learning curve, requires DevOps and infra setup |
| Ethereum Private | Startups and dev-friendly environments | Proof of Authority (PoA), PoS | Familiar tools (Solidity, Remix), strong ecosystem, fast prototyping | Lower privacy than Corda or Quorum, potential scalability issues |
| Corda | Financial institutions & regulated industries | Not blockchain-based (node-to-node agreement) | Designed for privacy, legal compliance, and high throughput | Less flexible for public chain use cases, smaller developer community |
| Quorum | Enterprises requiring Ethereum compatibility & privacy | Istanbul BFT, Raft | Ethereum-based but with privacy and permissioning, enterprise integrations | Limited community size, development led by specific vendors |
4. Define the Network Architecture
- Node Types: Identify node functions (e.g., validator nodes, endorser nodes, or standard nodes).
- Network Topology: Determine node interaction (e.g., centralized or decentralized topology).
- Access Control Mechanisms: Introduce access control mechanisms (e.g., Multi-Party Computing (MPC), and Attribute-Based Access Control (ABAC)).
5. Implement the Blockchain Infrastructure
- Set Up Nodes: Create and set up nodes while leveraging appropriate permissions and roles as needed.
- Smart Contracts: Write smart contracts to automate business logic and deploy as required.
- Security: Create encryption (e.g., SSL/TLS), authentication (e.g., use certificates or tokens).
6. Deploy Consensus and Validate
- Consensus Algorithm: Configure, deploy, and test your agreed upon consensus protocol.
- Transaction Validation: Define transaction validation rules and ensure only authorized nodes can validate transactions.
- Blockchain Explorer: Monitor your network with tools such as Hyperledger Explorer or Hyperledger Fabric.
7. Test the Network
- Unit Testing: Test individual components and smart contracts.
- Integration Testing: Test complete functionality as blockchains are made up of many interlinked components.
- Performance Testing: Test performance of transaction throughput, latency and scalability.
8. Deploy the Blockchain
- Production Environment: Deployment of your blockchain should be done based on a suitable infrastructure e.g. cloud, on-site or hybrid.
- Monitor: Monitors should be put in place to keep an eye on node performance, transaction throughput, and network health.
9. Maintenance & Updates
- Regularly Update the Platform: Ensure your blockchain technology and tools are regularly updated.
- Security Audits: Periodic evaluations of the blockchain for vulnerabilities.
- Scalability: Plan for future scalability and adaption of the blockchain design to match changing needs.
How Do Private Blockchains Work?

Private blockchains function similarly to public with one crucial difference – limited access. Only some participants are invited to join the network, usually stakeholders within an organization or consortium. Here’s how they work:
- Access Policies: Private blockchains provide limited access through an authentication layer. All participants must be screened and approved to interact or join the network.
- Custom Consensus Protocols: Instead of open consensus protocols like Proof of Work, private blockchains employ more efficient protocols, like Proof of Authority (PoA) or Byzantine Fault Tolerance (BFT), which enables speed and reliability.
- Higher Transactions per Second: Private blockchains generally accomplish higher transactions per second with significantly greater scalability due to a smaller number of nodes.
- More Privacy & Control: All transactions are conducted according to a predetermined set of rules designed by the controlling entity, allowing for greater control over data as well as the visibility and validity of transactions.
Future-proof your operations with a custom private blockchain!
From supply chains to internal finance, BlockchainTechnologies helps businesses unlock trust and transparency.
Benefits of Using a Private Blockchain for Your Business

A private blockchain offers businesses many operational and strategic advantages:
- Data Privacy: Sensitive data is protected and secured in a closed system.
- Regulatory Commitment: Participating entities can be controlled to ensure compliance with regulations.
- Cost: Lower transaction fees than a public network.
- Performance & Speed: Fast consensus leads to high throughput of transactions.
- Access Control: Granular control over who can read, write or validate.
- Audit Trails: Guaranteed, immutable audit logs provide proof of authenticity.
- Collaboration & Trust: In a shared system, trust among collaborating entities is improved.
Top Use Cases for Private Blockchain
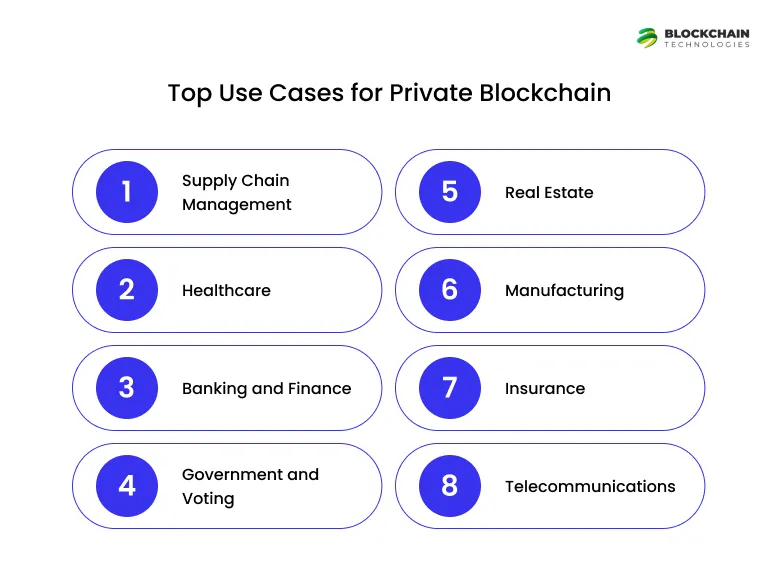
Where data privacy and process integrity are vital, private blockchains are best. Some interesting use cases include:
- Supply Chain Management: A permissioned blockchain for supply chain ensures every point in the supply chain can be tracked without the possibility of change or error.
- Healthcare: Patient records can be shared with providers while maintaining patient confidentiality.
- Banking and Finance: Transactions and settlements can be easier with secure audit trails to follow.
- Government and Voting: Secure citizen records or voting systems that cannot be tampered with.
- Real Estate: Transfers of ownership in properties, and smart contracts that outline conditions for leasing.
- Manufacturing: Encryption of vendors and production data to provide provenance.
- Insurance: Processing claims using verified information.
- Telecommunications: Management of inter-carrier settlement systems.
How We,Blockchain Technologies Assist You in Constructing a Private Blockchain Network?
Regardless if your private blockchain is deployed in the cloud, on-premise, or hybrid, we ensure enterprise-grade reliability through acceptance testing and continuous integration. End-to-end private blockchain development services assist companies in streamlining their processes, ensuring utilising trusted ledger technology promotes data integrity vs. traditional systems, and ensuring full control with permissions that enforce access—allowing companies to create the opportunity to redefine their business.
Get in touch today to schedule a free consultation and explore how we can help transform your vision into a powerful blockchain solution.
Private Blockchain Network FAQs
A private blockchain is permissioned, which means only verified entities can access it, making it more appropriate for enterprise applications where speed and data privacy are important. Public blockchains are accessible by anyone and can be more suited to decentralized apps instead.
Private blockchains can be extremely secure because of restricted access, limited access points, encryption of sensitive data using cryptographic algorithms (e.g., blockchain address, transaction receipts), and the adoption of consensus mechanisms like BFT or PoA (which ensures verification of transaction approval) that prevents unauthorized changes.
While having at least a theoretical understanding of blockchain architecture and smart contracts is helpful, there is a wide variety of well documented tools, applications and development environments (e.g. Hyperledger Composer, blockchain toolkits for Ethereum) available now that make it easier to deploy a private blockchain using drag and drop functionality.
The cost of a private Blockchain depends on which Blockchain platform is selected, how many nodes will be present, the level of custom development required, and the level of infrastructure. Small-scale deployment costs typically start around $5,000. Enterprise solutions tend to be considerably more, and can exceed $100,000.
Several industries utilize private blockchains. The finance, health care, supply chain, insurance, telecom, and real estate industries are all good candidates for private blockchains as they each rely on speed, privacy, and traceability.
Yes. With low-code tools, blockchain-as-a-service platforms, and expert development partners, even non-technical teams can launch a private blockchain.
Use open-source platforms like Hyperledger Fabric or Ethereum Private on cloud-based infrastructure. Costs can start as low as $500–$1,000 for basic MVPs.
A simple, private blockchain MVP can be developed and deployed in 4 to 6 weeks, depending on features and integrations.