Top Blockchain Applications Across Industries: Use Cases and Industry Examples
May 19,2025

Top Blockchain Applications Across Industries: Use Cases and Industry Examples
Blockchain technology transcends cryptocurrencies – it’s affecting industries the world over. Companies across sectors such as: finance; healthcare; supply chain; real estate; and media are investing significantly in blockchain because of its transparency and security.
For instance, blockchain applies to a variety of leading industries such as: finance; supply chain; healthcare; real estate; oil & gas; and media. In logistics and manufacturing sectors, “blockchain adds transparency and tracking, proving the authenticity. We’ll take a look at some specific examples in finance, logistics, healthcare, insurance, manufacturing, construction, government and entertainment. Furthermore we’ll see how blockchain proves to be valuable to solve real-world inappropriate business problems such as fraud prevention, traceability and smart contracts.
What Is Blockchain?
Blockchain is a decentralized, distributed ledger that links together blocks of immutable data and records transactions in a way that eliminates single points of failure and increases trust . Each block is linked to the preceding block with a cryptographic hash so that it cannot be altered. The consensus mechanisms such as Proof of Work (PoW) or Proof of Stake (PoS) will confirm there is consensus within the network on the validity of each transaction.
Why Blockchain Matters: Key Statistics?
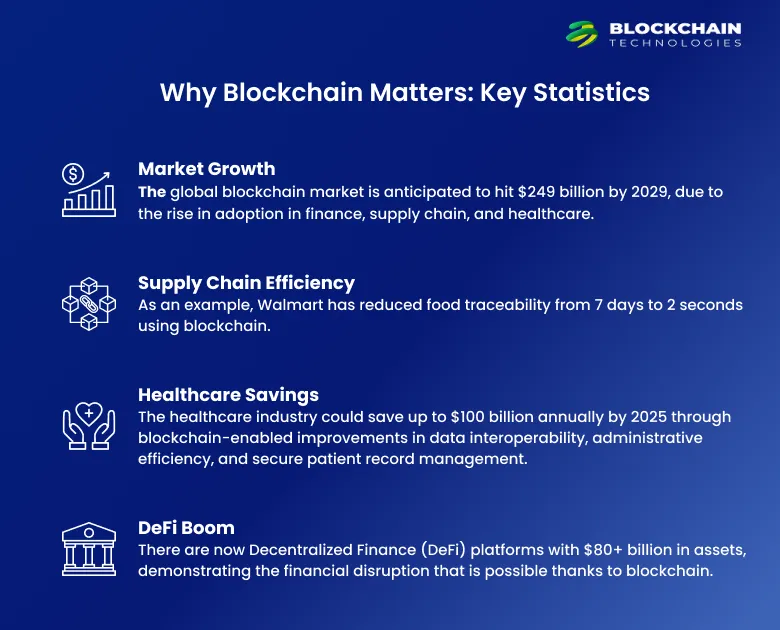
Market Growth: The global blockchain market is anticipated to hit $249 billion by 2029, due to the rise in adoption in finance, supply chain, and healthcare.
Supply Chain Efficiency: As an example, Walmart has reduced food traceability from 7 days to 2 seconds using blockchain.
Healthcare Savings: The healthcare industry could save up to $100 billion annually by 2025 through blockchain-enabled improvements in data interoperability, administrative efficiency, and secure patient record management.
DeFi Boom: There are now Decentralized Finance (DeFi) platforms with $80+ billion in assets, demonstrating the financial disruption that is possible thanks to blockchain.
Understanding Blockchain: Core Principles

Decentralization:
In centralized systems, a central authority manages and authenticates transactions across the system. Blockchain does away with having a central authority. Control and power are completely distributed across a network of numerous nodes. Every member of the network has access to the entire database, and all of its past information, eliminating the possibility of any one person having control of the entire chain. With its decentralized nature, we can be more trusting of one another in the network, and there is lower risk of centralized collapse or corruption.
Transparency: The transparent nature of blockchain makes it possible for all participants to see and verify the data recorded on the ledger. Each transaction is recorded in time and linked to a previous transaction so they form an unchangeable chain of records. Transparency develops accountability and trust in users; if there are any changes made to the data, all users will see this and have to validate it in agreement.
Security : Security is the most significant property of blockchain technology. Blockchain technology uses cryptography to enhance the security of data and transactions. Every block has a unique hash, the hash of the previous block, and connects to every preceding block. Therefore, it takes a drastic effort to go back to a previous block to change the information, let alone go back and change every block after the original block. To change one previous block and all the blocks going forward would be unrealistic, even if one wanted to gain control over the majority of the blockchain to verify a change occurred. Security makes blockchain legitimate for users and minimally vulnerable to changes to all pertinent data and transactions.
Immutability: Once data is written to the blockchain it is immutable. This finality provides an auditable and unchangeable record of events, something that is valuable in industries that involve reporting and accurate record-keeping, such as finance, healthcare, and supply chain management. Additionally, blockchain protects records from tampering or fraud because if someone even attempted to modify the data, it would be apparent to all network participants.
Efficiency: Blockchain also automates processes through smart contracts, self-executing contracts with the terms directly written into code. This reduces the number of intermediaries, decreases the speed of transactions, and decreases errors. To give an example, blockchain in supply chain, blockchain could automate the verification and transfer of products and both decrease the time delay, as well as increase operational efficiency.
Blockchain Use Cases Across Industries
Healthcare could benefit from blockchain’s ability to increase security and facilitate data sharing. Patient records and medical histories can be encrypted and stored on-chain allowing doctors and hospitals that have permission to access up-to-date records immediately . As all modifications to the records are stored on blockchain, tampering with the data becomes much harder. Pharmaceutical supply chains also can utilize blockchain to verify that drugs are not counterfeit and have been handled correctly.
Blockchain in Healthcare Usecases:
- Secure EMR Sharing – Patient info is stored on a decentralized ledger, making their electronic health records immutable. Doctors from different institutions would be able to view a patient’s encrypted history with no risk for unauthorized edits.
- Drug Traceability – Every step, from manufacturer to pharmacy, can be logged so patients can prevent counterfeiting of medications.
- Patient Identity Management – Blockchain enables self-sovereign IDs, allowing patients to control who sees their health information.
- Speeding up the claims process – by allowing providers to share verified medical data on-chain when insurers are processing health claims (aka, cheaper/faster)
Real time Example: Patientory
A platform for secure medical record storage and sharing that is HIPAA compliant through a blockchain layer of security. The software integrates into major EMR systems (Epic, Cerner), and has a mobile app to offer real-time health monitoring and communication with providers179.
Discover Blockchain's Impact on Healthcare
Explore how blockchain is revolutionizing patient care, data security, and clinical trials.
2. Blockchain in Manufacturing
Blockchain-related technologies are being used in manufacturing for quality control and supply chain integration. Each unique component and each batch of products can be tracked on a blockchain as they move through the plants, creating transparency, which makes recalls, and associated defect tracking/sourcing, easier. When a defect is uncovered, the exact production history gets recorded in real time, and a blockchain ledger of machine sensor data protects that proper production was followed every step of the way. Executives in manufacturing speak of real benefits being realized. In one survey 49% expect blockchain to provide better compliance, 31% see expanded market opportunity and, 28% expect diminished recalls.
Typical use cases are:
End-to-end track and trace: Each step, from raw ingredients to finished products, is documented.
- Automated purchasing: Smart contracts enable automatic ordering of parts or components when they fall below a purchase threshold.
- Inventory system: With decentralized ledgers, factories can see real-time inventory.
- Intellectual property protection: On-chain timestamps for design specifications protect against intellectual property theft.
- Equipment warranty tracking: Machine service histories, maintenance logs, and warranty claims can be recorded on a blockchain to verify that the servicing has been completed.
By combining the power of the IoT with smart interoperable blockchains, manufacturers have achieved a “trusted data highway” as transactions occur on the production line. Blockchaintechs.io has assisted companies in establishing private ledgers, by connecting suppliers and manufacturers, ensuring provenance and production efficiency.
Real time Example: 1. Walmart & IBM Food Trust
The Traceability of Food Reformation.
Application: Food traceability for products (e.g. mangoes, leafy greens) to track from farm through blockchain to shelf.
Impact: Traceability time improved from 7 days to 2 seconds for recalls and food safety
Technology: IBM Hyperledger Fabric records origin, batch numbers, and shipping information. Suppliers, including Tyson Foods and Dole participating provide real-time information.
3. Blockchain in Insurance
Insurance companies deal with fraud and inefficient processes that blockchain can address. Insurance products and claims can be ‘on-chain.’ Using a shared blockchain ledger for policies and claims can make records immutable and transparent. All insurers looking at the same blockchain record can eliminate fraud (think multiple claims for one loss). Smart contracts can facilitate automated claim payouts: imagine a contract for an accident insurance product that can auto-payout when verified police and repair records are on-chain.
Blockchain in Insurance: Use Cases
- Fraud prevention: Common blockchain claims ledgers eliminate duplication. Indeed, fraud costs are enormous (estimated at $40B per year in the U.S.) that blockchain can significantly reduce.
- Automated claims: Policies written in smart contracts, automatically execute payment when conditions of the contract are met; thereby expediting customer payouts and subtracting processing costs (BCG estimates savings of $200B per year).
- Transparent risk pooling: Reinsurance companies can write contracts on a blockchain and capture catastrophic risk easily.
- Health and crop insurance: Ability to trust share sensitive medical data or local weather-related data enables the insurer to process claims much faster. For example, a blockchain can support encryption on patient data and leverage that data for insurance health insurance decisions.
- Microinsurance: Parametric insurance (like crop/weather insurance necessary for farmers) can be fully automated on blockchain.
Carriers can improve trust and reduce administrative costs by considering “blockchain use cases in insurance.” We regularly suggest insurers pursue a blockchain ledger for one line of business — and we have a blockchain development partner that provides integration and security auditing services.
Real time Example : Parametric Insurance: Lemonade’s Crop Protection
The Lemonade Foundation, along with its partners Avalanche and Chainlink, have launched blockchain-based parametric crop insurance for farmers in Africa. The smart contracts facilitate automatic payouts based on weather data from Internet of Things sensors and APIs (for example, drought detection).
Impact: It reduces claims management costs by 90%, allowing for lower premiums for smallholder farmers while allowing for fast payouts when things go wrong.
4. Blockchain in Construction
The construction industry is using blockchain as a means for achieving data integrity and more efficient workflows. All project documents (contracts, blueprints, change orders, etc.) can be hashed and stored on the blockchain, thereby establishing immutable documentation. Documentation that cannot be modified provides an immutable audit trail that supports any disputes or claims, because every update or change is documented. Similarly, materials and equipment can be tracked through the supply chain. For example, steel quality certification can be tracked and a smart contract can automatically pay a supplier as soon as delivery is accepted.
Blockchain in Construction Use cases:
- Document security: Important project documents are held on blockchain eliminating risk of unauthorized alteration.
- Supply chain & payments: Material delivery can be recorded on-chain with smart contracts releasing payments when criteria are fulfilled.
- Project management: The shared ledger provides architects, contractors and clients with a real-time update enabling direct collaboration.
- Certification of materials: Certificates for equipment and materials (e.g. compliance tests) can be time-stamped by the blockchain for easy record retrieval and audit.
- BIM integration: The use of blockchain provides assurance that all participants in a BIM environment have access to the current approved designs.
Construction companies seeking “blockchain for construction” as a solution should consider executing pilot projects that will automate payments or documentation as they will have a returns on investment (ROI) in short order. A partner like Blockchaintechnologies can customize blockchains to construction project workflows and incorporate industry regulatory requirements.
Real time example : BuildCoin Foundation
The BuildCoin Foundation is a nonprofit using blockchain for the funding and management of construction projects, particularly in affordable housing. The BuildCoin project tokenizes building projects, allowing for microfinancing, enabling individuals and organizations to invest in building projects. This model increases transparency, speeds up the funding process and community involvement leads to project completion faster.
5. Blockchain in Government and the Public Sector
With agencies around the world trying it for the sake of transparency and trust, government agencies and public sector organizations are likely the most explored use cases for blockchain. Take absentee ballot e-voting; through blockchain technology, each ballot could be recorded in a way that renders votes immutable and verifiable. West Virginia’s e-voting pilot in 2018 — using blockchain to record absentee ballots — is one example of this process.
Moreover, governments are piloting blockchain IDs and registries. Countries and even cities in their entirety (e.g. Dubai) are experimenting with blockchain for land titles, identity and more, decreasing fraud and administrative costs significantly in these areas. Other use cases for the public sector comprise:
- E-Governance: Public records, including land records, court documents and licenses that are accessible to verify by both the citizen and agency.
- Digital identity: Blockchain based IDs could allow citizens to securely prove they are who they say they are, while only having access to the government services that they require, without revealing personal data.
- Voting systems: Possessing immutable records of votes establishes an immutable foundation to the electoral process and integrity.
- Supply & Aid Tracking (i.e. Public procurement, aid distribution – see e.g. the UN’s World Food Programme is already using blockchain to transparently ensure that food supply is administered accurately).
- Tax & Customs: A blockchain that records any trade documents could create automated customs duty and defeat tax evasion.
These are just a few “blockchain use cases in government.” My advice is for public-sector CIOs to collaborate with informed and conscientious developers. Blockchaintechs.io offers consulting on regulatory compliance and can build permissioned blockchains for civic-type applications. Explore our Blockchain Consulting Services.
Real time Example: Estonia’s e-Government System
- Use Case: Estonia uses blockchain to secure its government data (health records, court systems, police records, and legislative processes).
- Impact: Every citizen’s health, judicial, legislative, and security data is protected using blockchain for integrity and real-time verification.
- Official Website: E-Estonia.com
6. Blockchain in Media and Entertainment
Blockchain is changing the digital media space by returning power to creators. Blockchain in the music industry and publishing, artists can register their content on-chain so streams or sales start triggering fair, automated royalty splits. As one analysis pointed out, blockchain “can bring democracy and transparency to music-related payments and royalties”. Blockchain also powers the explosion of NFTs and tokenized content: digital art, collectibles, and even virtual event tickets being exchanged as blockchain assets.
Blockchain in Media and Entertainment Use Cases:
- Royalties and licensing: Smart contracts distribute royalties in real-time as a song is played or content is streamed.
- Copyright protection: Platforms like Binded timestamp creative works on-chain, so authors can proactively prove ownership.
- Content distribution: By distributing and selling media (music, video) directly to a consumer as tokens on the blockchain, intermediaries are removed from the process.
- Fan engagement: Artists are issuing tokens or NFT collectibles to engage their communities and fans (i.e. a fan club could issue a proof of membership token or offer fans exclusive content).
- Decentralized streaming: Streaming services that pay artists in crypto per play.
Real Time Example: Audius – Decentralized Music Streaming
- Use Case: Audius is a blockchain-based music streaming platform that allows artists to publish their music directly to fans without intermediaries.
- Impact: By leveraging blockchain, Audius ensures transparent royalty distribution and empowers artists with greater control over their content.
- Website: Audius.co
7. Blockchain Use cases in Supply Chain
Blockchain is transforming global supply chains by making transactions and logistics more transparent, traceable, and secure. From raw materials to final product delivery, blockchain allows stakeholders to record each step of a product’s journey immutably. This minimizes fraud, ensures compliance, and builds trust among consumers. As supply chains become increasingly complex and globalized, blockchain acts as a single source of truth shared across suppliers, manufacturers, distributors, and retailers.
Blockchain in Supply Chain Use Cases:
- Product traceability: Track the origin and movement of goods in real-time—from raw materials to finished products—to verify authenticity and ethical sourcing.
- Counterfeit prevention: By placing serial numbers and certifications on the blockchain, companies can prove product legitimacy and reduce fraud.
- Inventory management: Blockchain combined with IoT devices helps optimize inventory tracking and automation across warehouses and shipments
- Supplier verification: Blockchain can store supplier certifications and audit trails to ensure ethical and sustainable sourcing.
- Smart contracts for logistics: Automatically trigger payments, customs clearance, or restocking when predefined conditions are met.
Real Time Example: IBM Food Trust – Transparent Food Supply Chain
- Use Case: IBM Food Trust is a blockchain platform that connects farmers, processors, distributors, and retailers in the food industry to improve transparency and safety.
- Impact: By using blockchain, companies like Walmart can trace food items like lettuce or pork from farm to shelf in seconds—improving food safety and speeding up recalls.
- Website: ibm.com
Other Emerging Use Cases and Industries
Outside of the “heavy” industries, we will soon see blockchain applications in many other areas:
- Energy & Utilities: Decentralized energy grids, where consumers can trade peer to peer energy (a good example is Power Ledger, operating in Australia).
- Intellectual Property: Blockchain will allow the author of any digital content and even patents, to prove their authorship on blockchain (e.g. digital art, or research publications).
- Cybersecurity: Blockchain can be used to secure sensitive data logs. Guardtime has been using distributed ledger technology to validate data integrity in government and enterprise security.
- Sustainability: Blockchain can be used to track carbon credits transparently or recycle chains (Ecolife Recycling is using blockchain to manage their waste transparently).
- Agriculture: Smart contracts for microloan and homemade produce (farm-to-table systems).
- NFTs and Metaverse: Beyond art, NFTs represent the ownership for virtual real estate, gaming assets, and community governance (DAOs).
- IoT Integration: Blockchains can coordinate autonomous IoT device networks, ensuring tamper-proof data sharing.
Estimate Your Blockchain Project Costs
Get a quick estimate for developing your blockchain solution.
How to Choose a Right Blockchain Development Company?
Implementing blockchain properly and successfully involves expertise. As one industry expert succinctly puts it, every particular area and market “will need specialized expertise to unlock blockchain” value. There are a number of key components to think about when selecting a blockchain development companies(for Web3 /Blockchain consulting or full-stack DApp development):
- Industry expertise: The development firm should have expertise and knowledge around your industry (such as finance, supply chain) to guide your use case.
- Technical skills: The firm should be proficient in at least Ethereum, Hyperledger, Solana or whatever other relavant platforms, plus security best practices.
- Compliance & security: Ensure the firm has an understanding of compliance regulations (e.g. for health (HIPAA) or data obligations (GDPR)).
- Agile methodology: Look for a partner who can rapidly build a prototype, test it in real-world scenerios and iterate.
- Full-service offering: Most of the best firms (including Blockchaintechs.io) will handle everything from strategy to launch, including UI/UX and integration consideration.
Choosing a partner is an important decision. Blockchaintechs.io, for example, produces end-to-end Web3 development services. So, we can help you craft a blockchain roadmap and allow us to build the distributed solutions you need for your business. And remember, blockchain projects are not just about the technical code; they include legal, security and change-management considerations to be successful.
Find the Right Blockchain Development Partner
Discover tips for selecting a reliable blockchain development company.
Conclusion
Blockchain technology is now moving from a buzzword to a business must-have. Be it in finance, supply chain, healthcare, government, and many other sectors, “blockchain technology is changing the way an industry operates globally. The market is forecasted to explode – one report claims the blockchain industry will hit $152 billion by 2029- as more and more industries adopt its use. Organizations that recognize these use cases will reduce costs, trust, and gain a competitive advantage.
At Blockchaintechs.io, our mission is to assist businesses in leveraging blockchain and Web3. We offer blockchain development, smart-contract engineering, DeFi Development, NFT Marketplace Platforms, and much more – from startups to enterprise-level organizations. If you find these use cases inspirational for using a blockchain application and would like to learn more about using it in your business, please reach out to us and let’s start. Seriously!
Reach out to our team to build your blockchain project and put into motion the potential we just touched on above.
FAQs
Some examples of how blockchain is changing health care are:
- Secure Medical Records: Services like Medicalchain and Patientory allow patients to control who accesses their EHR.
- Drug Traceability: The blockchain used by IBM is tracking pharmaceuticals to help reduce the incidence of counterfeits (ex. MediLedger).
- Clinical Trials: Embleema is tokenizing a patient’s data to help with research and the consent process around it.
Key trends include:
- Provenance: Walmart was able to reduce food traceability from 7 days down to 2 seconds using IBM Food Trust.
- Anti–Counterfeiting: De Beers uses Tracr to guarantee that their customers know they are sourcing ethical diamonds.
- Automated Payments: BMW uses PartChain to arrange automatic payments to suppliers using smart contracts.
Some examples of blockchain’s benefits to finance include:
- Cost-Efficiency: Lemonade’s parametric insurance has cut claims costs by 90%.
- Fraud Prevention: Allianz is using the blockchain to prevent duplicate claims.
- Transparency: Decentralized finance (DeFi) lending protocols, like AAVE, no longer need intermediaries to facilitate auto lending.
Costs will vary depending on:
- Complexity: Simple supply chain tracking ($15,000-$150,000) vs. an enterprise solution ($150,000 and above).
- Platform: Public blockchains (Ethereum) have a lower upfront burden but has transaction fees. Private blockchains (Hyperledger), on the other hand, are the opposite.
- Integration: Adding legacy system upgrades accounts for 20-30% in addition to other initial budgets as well.
Public (e.g., Ethereum): Open to be viewed, decentralized approach, transparent, but slow. Costly for enterprises to transact.
Private (e.g., Hyperledger): High speed; Modular & Tailorable, able to comply with regulations such as HIPAA
Pilot Projects: 3-6 months (e.g., Dubai’s “blockchain cargo” system).
Full Deployment: 12-18 months for use on enterprise level solutions.
Yes. There are API’s and middleware (e.g., Chainlink oracles) for connecting blockchain solutions to existing legacy databases, IoT devices or a cloud platform now integrates with.
