Exploring DePIN: Real-World Applications of Decentralized Physical Infrastructure Networks
May 19,2025
Exploring DePIN: Real-World Applications of Decentralized Physical Infrastructure Networks
As our global infrastructure starts to show its age and centralized systems face more vulnerabilities, a wave of innovators is looking to DePIN—Decentralized Physical Infrastructure Networks—to change the way we construct and manage physical systems. Messari reports that the DePIN sector boasted a market cap of over $20 billion in 2024, with promising growth expected as we move into 2025, driven by the rising adoption of decentralized wireless (DeWi), energy, storage, and sensor networks.
While blockchain is often associated with cryptocurrencies and DeFi development, its application in physical infrastructure through DePIN represents a major shift. This method not only decentralizes digital data but also redefines how we govern and monetize real-world assets like power grids, wireless towers, and storage facilities. In this blog, we’ll dive into how DePIN operates, its key advantages, emerging use cases with real-world examples, and what we can anticipate from this technology in 2025 and beyond.
What is DePIN ?
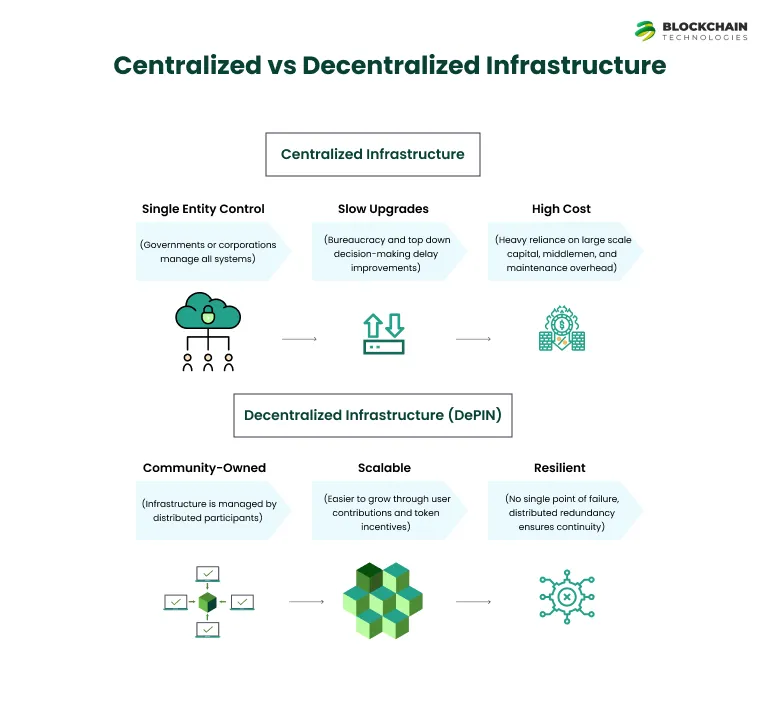
DePIN stands for decentralized physical infrastructure networks. These networks use blockchain-based incentives to coordinate, fund, and manage physical assets. Unlike the traditional centralized systems where governments or corporations hold all the power over physical resources, DePIN projects promote shared ownership and management through token economies and peer-to-peer infrastructure sharing.
Some examples of DePIN in action include decentralized wireless networks, open charging stations for electric vehicles, and solar power microgrids governed by blockchain. With DePIN, communities can come together to create and sustain real-world infrastructure without having to depend on monopolies or central authorities.
What is Decentralized Infrastructure?
Decentralized infrastructure refers to physical or digital systems that are owned, operated, and maintained by a distributed network of individuals, communities, or organizations—rather than centralized governments or corporations. These systems use blockchain technology and token-based incentives to coordinate participation, governance, and rewards. Unlike traditional infrastructure that relies on top-down control, decentralized infrastructure enables scalable, bottom-up innovation and democratized access.
Centralized vs Decentralized Infrastructure: A Quick Comparison

Key Benefits of Decentralized Infrastructure Using DePIN
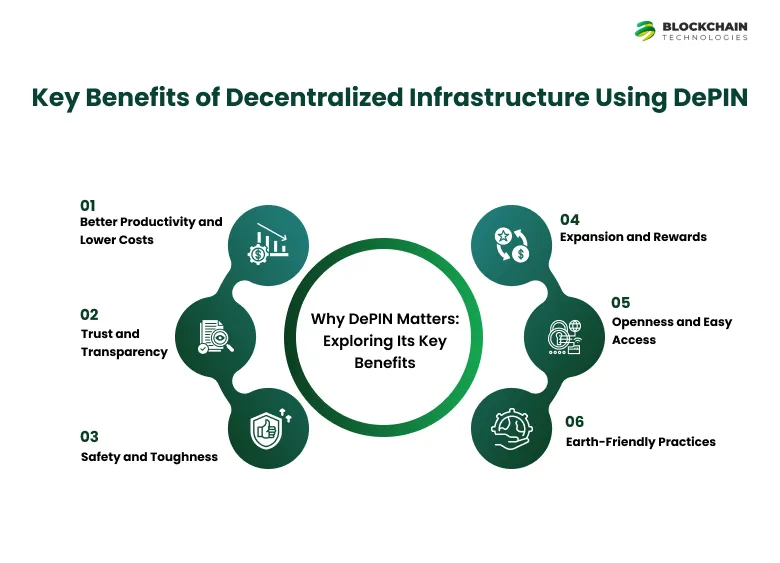
Decentralized Physical Infrastructure Networks (DePIN) have an influence on how we design and maintain infrastructure. DePIN makes systems more effective, sparks new ideas, boosts access, and supports sustainability for the long haul. Here are some of the main perks:
1. Better Productivity and Lower Costs
DePIN cuts out unnecessary middlemen and top-down management systems to streamline infrastructure operations. Traditional centralized setups often get bogged down by red tape and too many layers of bosses. DePIN, on the other hand, lets people work together , which cuts costs and speeds up tasks and services.
2. Trust and Transparency
Using blockchain’s unchangeable record, DePIN makes sure all deals and exchanges within the network are logged and checkable. This transparency builds trust and cuts down on the chance of cheating or misuse, as members can check activities on their own.
3. Safety and Toughness
DePIN’s main strength comes from its spread-out structure, which makes the system tougher. By sharing tasks across many separate points, it lowers the risk of everything failing at once making the network better at standing up to online attacks physical breakdowns, or natural disasters.
4. Expansion and Rewards
DePIN models offer financial rewards to encourage people to join in. They give out tokens or credits to those who add resources. This setup motivates both people and companies to help build keep up, and grow the network. It leads to natural growth and new ideas.
5. Openness and Easy Access
DePIN is open to all kinds of players—big companies and regular folks alike. It gives anyone with the right tools a chance to add things like internet speed, storage space, or green energy. This open approach lets more people join in and makes it easier for everyone to use these services.
6. Earth-Friendly Practices
A lot of DePIN projects are built to be eco-friendly using clean power like solar, wind, or water. These -friendly setups lower their carbon footprint and push for energy-saving tech throughout decentralized systems.
Ready to Build the Next DePIN Innovation?
Whether you’re launching a decentralized energy grid or a community-powered network, our team helps you design, build, and scale the infrastructure of the future.
How Decentralized Networks Improve Physical Infrastructure
DePIN models use blockchain to replace legacy coordination mechanisms with automated, community-governed alternatives. This leads to faster deployments, localized decision-making, and real-time optimization of resources. For instance, decentralized wireless networks bypass telecom monopolies, while tokenized energy grids allow peer-to-peer energy trading. These networks don’t just improve infrastructure—they modernize how it’s financed, managed, and scaled.
Key improvements include:
- Dynamic resource allocation via smart contracts
- Reduced operational costs due to peer incentives
- Faster scaling through community-driven node deployments
How Does the DePIN Network Work?
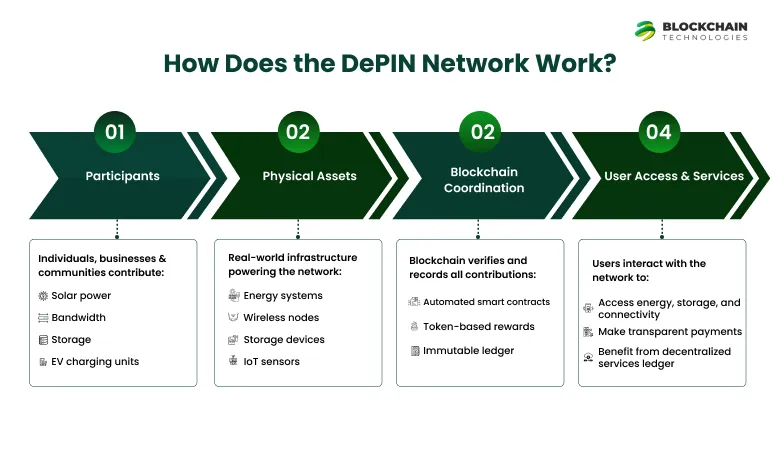
A DePIN network runs through teamwork among many stakholders and technologies, all linked by blockchain. These parts together build a spread-out, safe, and reward-driven system that can manage real-world setups on a big scale.
1. Partcipants and Resource Contributor
Every DePIN network has its core: the people—folks, groups, and companies who give key resources. These might be machines like routers and EV chargers green power like sun or wind, or computer stuff like storage, number-crunching power, or internet speed. The spread-out model lets anyone join and back the network making a lively and open setup.
For example, users can share extra power from their rooftop solar panels spare storage from their personal computers, or even wireless nodes set up by communities. These shared resources come together to create a strong spread-out network—without needing a central manager.
2. Blockchain as the Coordination Layer
Blockchain serves as the basic structure for DePIN. It logs every deal, exchange, and input with unchangeable precision making sure everything stays safe and clear. It gets rid of the need for centralized oversight while building trust between users.
Blockchain also enables token-based rewards—people who contribute get digital tokens in return for taking part. Users can trade these tokens, hold onto them, or use them to get services creating a network that keeps itself going and makes value.
3. Physical Infrastructure Assets
While blockchain plays a key role in coordination, the physical assets define what the network does. These assets include solar power systems, telecom towers spread-out data centers, and networks of sensors. Let’s look at decentralized power grids as an example: a home with solar panels can send extra electricity to the network. In a spread-out storage setup, someone might rent out their spare hard drive space to others using a blockchain-powered app. When combined , these assets become part of a synced efficient infrastructure system.
4. Smart Contracts and Automation
Smart contracts are digital agreements that run by themselves on the blockchain. They make the network’s rules work, making sure people get paid, services are delivered as promised, and everything runs. Let’s take an example. In a network of EV charging stations that no one company controls, a smart contract could check if power was delivered and send tokens to the provider’s wallet—without anyone watching over it. This automatic process cuts down on hassles, saves money, and makes the system more dependable.
DePIN Development Services for Startups & Enterprises
Get full-stack support—from tokenomics to hardware integration—to launch your decentralized infrastructure project faster.
Real-World Use Cases of Decentralized Infrastructure (DePIN)
DePIN combines blockchain tech with physical infrastructure to build community-driven decentralized systems. Here are key use cases with real-world applications of DePIN backed by current projects and trends as of 2025:
1. Decentralized Wireless Networks (DeWi)
DePIN allows wireless connectivity between peers skipping traditional telecom providers.
- Helium Network: A trailblazer in DeWi, Helium lets users set up hotspots for IoT connectivity giving $HNT tokens to contributors. By 2025, it boasts over 335,000 hotspots worldwide and has branched out into mobile services with Helium Mobile.
- Uplink: Zeroing in on AI-driven connectivity, Uplink is creating a decentralized wireless network on Avalanche aiming for business-grade growth and compatibility.
2. Decentralized Energy Grids
DePIN makes energy distribution more open through blockchain-powered trading between individuals.
- PowerLedger: A system that lets people with solar panels sell extra energy to their neighbors using blockchain cutting down on the need for big power grids
- Community Microgrids: Projects in California and Europe use DePIN to match renewable energy supply with demand, combining solar panels and batteries to make local areas more self-reliant
3. Decentralized Data Storage
DePIN turns cloud storage into a spread-out, cheaper option.
- Filecoin: People rent out spare storage space worldwide earning FIL tokens. The system keeps data safe through cryptographic proofs (Proof of Spacetime and Replication), with storage capacity set to exceed 23 exbibytes (EiB) by 2025.
- Arweave: Focuses on storing data forever handling over 1.28 billion transactions in 2023 and growing into decentralized archiving solutions.
4. Sensor Networks for Smart Cities
DePIN uses scattered sensors to gather and profit from real-world data.
- Hivemapper: People use dashcams to map roads and earn HONEY tokens when they share location data. This builds a distributed option to Google Maps covering over 94% of city areas
- XYO Network: More than 8 million nodes give Proof of Location info, fighting GPS faking in shipping and enhanced reality
5. Distributed Computing Power
DePIN pools unused computing resources for high-demand jobs.
- Render Network: Artists and studios get GPU power for 3D rendering, paying contributors in RENDER tokens. The network moved to Solana in 2024 to scale up, helping industries like gaming and VR.
- Bittensor: A decentralized AI network where people train machine learning models and earn TAO tokens based on the value of data they add.
6. Logistics and Supply Chain Optimization
DePIN makes global logistics clearer and effective.
- DIMO: Car owners share live car data (like gas mileage and repairs) through IoT gadgets. They earn tokens while making fleet management better.
- Meson Network: A place to buy and sell extra internet bandwidth. This cuts costs for decentralized apps.
7. Healthcare Infrastructure
DePIN backs decentralized healthcare answers for sharing data and remote care.
- CUDIS Ring: A project powered by Helium to allow safe decentralized health data swapping and IoT device control for telemedicine.
- Patient Data Sovereignty: Systems let patients keep medical records on DePIN networks. They can give access to doctors using token-based permissions
8. Decentralized Telecommunications
DePIN has an impact on global connectivity to meet AI and IoT needs.
- World Mobile: Brings internet to Africa through decentralized nodes, giving tokens to contributors.
- NATIX Network: Uses AI and DePIN to provide up-to-date traffic info helping self-driving cars and city planning.
9. Tokenized Infrastructure Ownership
DePIN allows people to own parts of physical assets using blockchain.
- Solar Panel Co-Ownership: People can buy shares in tokenized solar farms, getting money from energy sales and supporting green infrastructure
- Shieldium: A cybersecurity DePIN where users share server resources to shield Web3 systems, earning $SDM tokens
10. Environmental Monitoring
DePIN networks keep tabs on climate data to support sustainability efforts.
- WeatherXM: A weather station network owned by the community where people who contribute earn tokens for providing very local climate data, which finds use in farming and responding to disasters
Curious About Cost & ROI for DePIN Projects?
Understand how DePIN can cut costs and accelerate returns. We’ll send you a free cost-benefit breakdown tailored to your use case.
Challenges in the Usage of DePIN
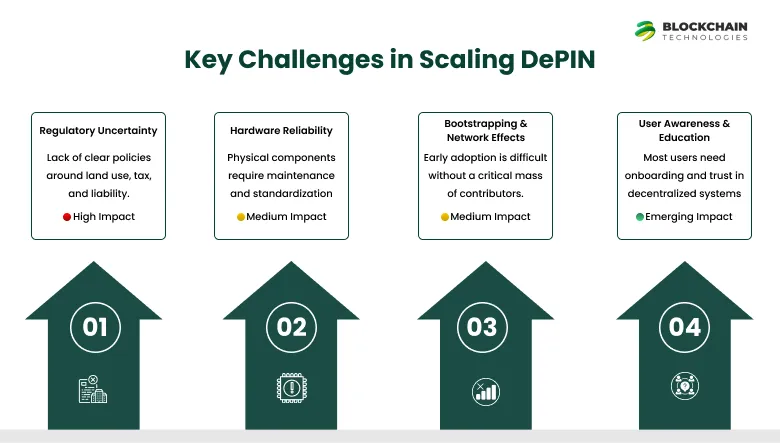
Even though DePIN shows promise, it faces several obstacles in its adoption. As these systems grow, tackling these issues becomes crucial:
1. Regulatory Uncertainty
Many countries don’t have clear laws for decentralized physical infrastructure. Issues about land use, who’s responsible, taxes, and working across borders still make it hard to implement on a big scale.
2. Hardware Reliability and Maintenance
DePIN depends on physical devices, so it has to deal with problems like upkeep, making sure things work well, and keeping performance steady in different parts of the world.
3. Bootstrapping and Network Effects
New DePIN networks need early supporters and reasons to join to get going. Without enough people, they might not get used to much or be able to keep running.
4. User Awareness and Education
DePIN brings new ideas to the table. These ideas need explaining to users, building trust, and giving tech help—for people who aren’t tech-savvy.
What Does It Cost to Build a DePIN Network?
The cost of launching a DePIN project depends on multiple factors:
- Hardware requirements (routers, IoT devices, EV stations)
- Blockchain layer integration(Ethereum, Solana, Avalanche, etc.)
- Smart contract development
- Tokenomics and governance
- User interfaces (mobile/web apps)
Typical pilot DePIN projects start at $10,000–$50,000 depending on scope and scale. At Blockchaintechnologies, we offer modular pricing based on your project’s specific needs—from MVP launches to full-scale infrastructure rollouts.
Final Words
Decentralized Physical Infrastructure Networks (DePIN) have an impact on how we view public infrastructure—from who owns it to how we carry it out. DePIN uses blockchain to spur contributions, streamline teamwork, and check trust. This opens up new ways to boost output and create chances across energy, communications, data, and transport.
While obstacles exist, networks like Helium, Filecoin, and Power ledger keep doing well. This proves that the model isn’t just an idea—it works and can grow. As rules become clearer and more people join in, DePIN will become a key part in how global infrastructure changes. Now’s the time for companies, coders, and rule-makers to look into what DePIN can do and help shape its future.
Ready to Build Your Decentralized Infrastructure Network?
From tokenomics to sensor integrations, our expert team builds scalable, blockchain-powered DePIN systems tailored to your goals.
FAQs
DePIN means Decentralized Physical Infrastructure Networks. These are systems where the community owns and runs real-world infrastructure using blockchain tech.
Unlike centralized infrastructure that governments or big companies manage, DePIN lets people own a share, earn tokens, and have a say in how things are run.
Helium for wireless Filecoin for cloud storage Power ledger for energy trading, and Peaq for getting around and moving goods.
Energy, telecommunications, cloud computing, transportation, and logistics are early adopters seeing big gains.
Yes. New mixed models are popping up where DePIN layers boost or fine-tune traditional infrastructure with spread-out control and rewards.

